Introduction: Severe weather events can have a profound impact on our lives, safety, and communities. In this special addition to our weather education series, we’ll explore the world of severe weather, including the types of severe weather phenomena, the conditions that lead to their formation, and how to stay prepared when severe weather strikes.
Types of Severe Weather: Severe weather encompasses a range of dangerous meteorological phenomena. Some of the most common types include:
- Thunderstorms: Thunderstorms are often accompanied by lightning, heavy rain, strong winds, and sometimes hail. Severe thunderstorms can lead to flash floods, wind damage, and tornadoes.
- Tornadoes: Tornadoes are violently rotating columns of air that extend from thunderstorms to the ground. They are capable of causing devastating damage, with varying intensities rated on the Enhanced Fujita (EF) scale.
- Hurricanes and Tropical Cyclones: These powerful storms, which form over warm ocean waters, can bring destructive winds, torrential rain, storm surges, and widespread flooding.
- Flash Floods: Flash floods occur when heavy rainfall overwhelms drainage systems, leading to rapid and dangerous flooding. They can result from severe thunderstorms, hurricanes, or even heavy rainfall over a short period.
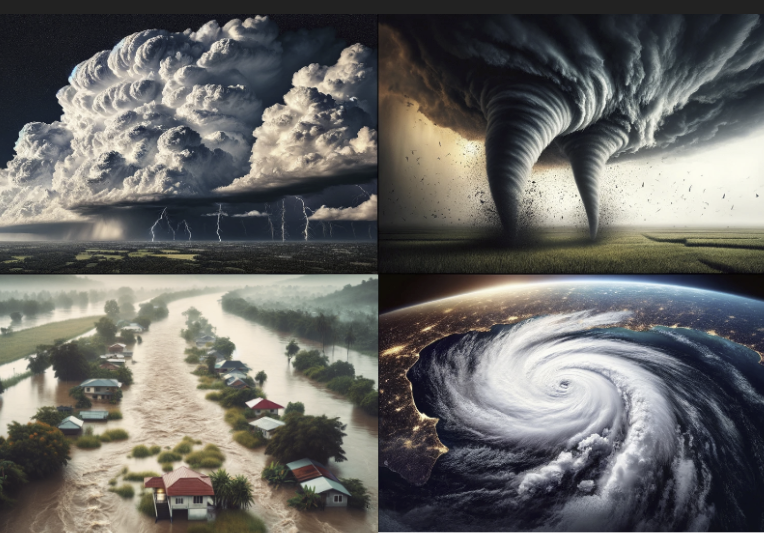

Conditions for Severe Weather: Severe weather events are driven by specific atmospheric conditions. Understanding these factors can help predict and prepare for severe weather:
- Instability: Severe weather often occurs when warm, moist air near the surface rises and interacts with cooler, drier air aloft, creating instability that fuels thunderstorms and tornadoes.
- Moisture: Adequate moisture in the atmosphere is essential for the development of severe storms and heavy rainfall.
- Wind Shear: Wind shear refers to changes in wind speed and direction with altitude. Strong wind shear can enhance thunderstorm development and the formation of rotating supercells, increasing the risk of tornadoes.
- Fronts: The collision of different air masses, such as a cold front meeting a warm front, can trigger severe weather events.
Staying Prepared: Being prepared for severe weather is essential for your safety and well-being. Here are some tips to stay prepared:
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and warnings issued by the National Weather Service (NWS) or your local meteorological agencies.
- Emergency Kit: Create an emergency kit with essential supplies, including water, non-perishable food, flashlights, batteries, a first-aid kit, and important documents.
- Emergency Plan: Develop a family emergency plan that includes a designated meeting place and communication strategy.
- Alert Systems: Download the NickelBlock Forecasting app and consider investing in a NOAA Weather Radio.
- Safe Shelter: Know the safest place to seek shelter during severe weather events, such as a basement or an interior room on the lowest floor.
Take Home: Severe weather is a formidable force of nature that demands our respect and preparedness. By understanding the types of severe weather, the conditions that lead to their formation, and how to stay safe, we can navigate through these events with resilience and protect our communities.
We hope this overview of severe weather has been informative and useful for your safety and preparedness. If you have further questions or topics you’d like us to explore, please feel free to reach out. Stay vigilant, stay prepared, and stay safe when severe weather strikes!